Sleep Stages Guide: The Science Behind Better Rest
Learn how your body cycles through 4 sleep stages each night and discover practical ways to wake up truly refreshed.
Ever wake up after 8 hours feeling like you got hit by a truck? The problem isn't always how long you sleep - it's what happens during those hours.
Your brain doesn't just "shut off" at night. Instead, it orchestrates an intricate dance through different sleep stages, each one crucial for your physical recovery, mental clarity, and emotional balance.
In this guide, you'll discover exactly how these sleep stages work, why each one matters, and most importantly - practical ways to optimize your sleep cycles so you actually wake up refreshed. Let's dive into the science that could transform your nights (and your days).
Summary
- Understanding The Four Sleep Stages
- Stage 1: Your Sleep Entry Point
- Stage 2: Where You Spend Most Time
- Stage 3: Deep Sleep Recovery Mode
- REM Sleep: The Dream Factory
- How Sleep Cycles Progress Through Night
- What Disrupts Your Sleep Stages
- Optimize Your Sleep Architecture
- Sleep Disorders That Break Cycles
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
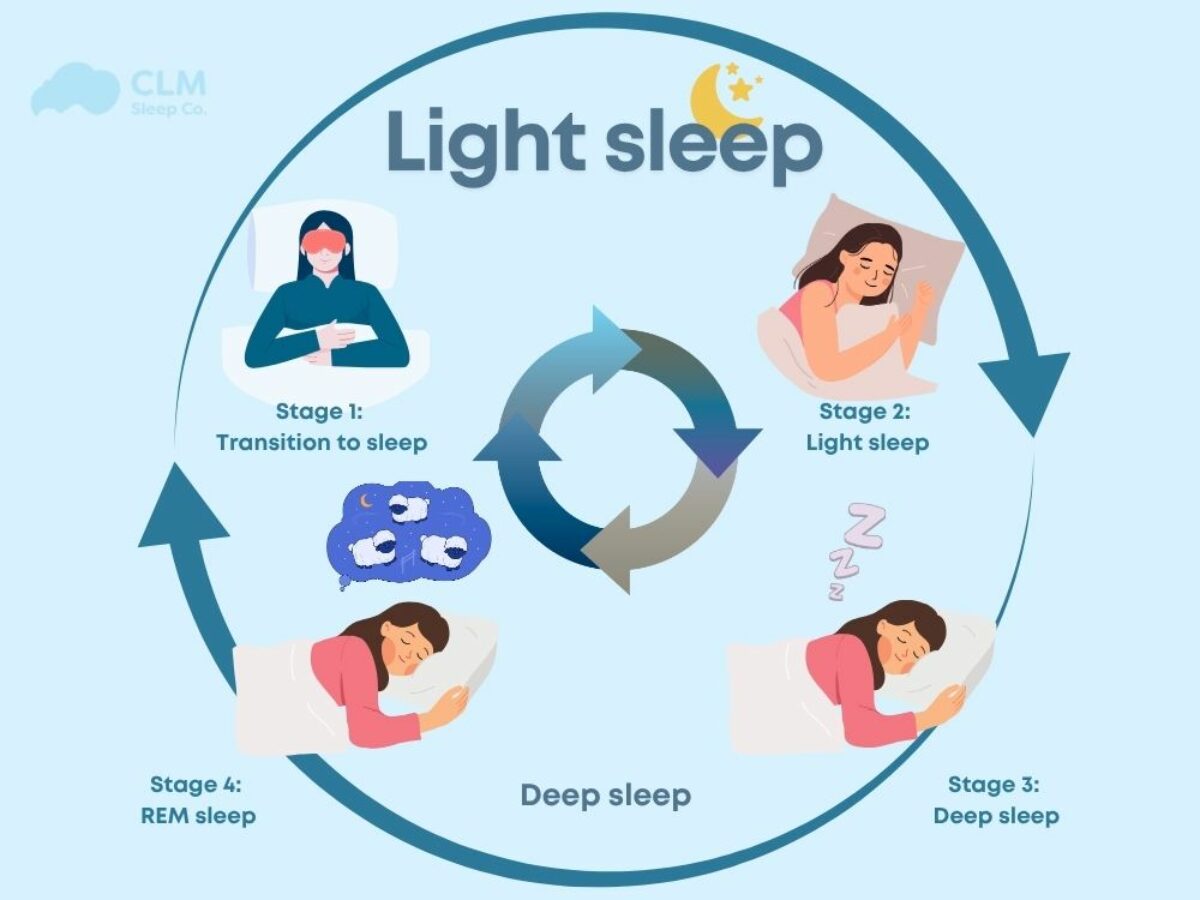
Understanding The Four Sleep Stages
Sleep isn't one continuous state. Think of it more like a playlist that shuffles through four distinct tracks all night long.
These stages split into two main categories: non-REM (stages 1, 2, and 3) and REM sleep. Each stage has its own brain wave patterns, physical changes, and specific jobs to do for your body and mind.
During a typical night, you'll cycle through all four stages about 5-6 times. Early cycles are heavy on physical recovery, while later ones focus more on mental processing and dreams.
Here's what makes this fascinating: the quality of your sleep depends less on total hours and more on how smoothly you progress through these stages without interruption.
Your body knows what it needs. When you're sick, you'll spend more time in deep sleep for immune recovery. When you're learning something new, your brain extends REM periods for memory consolidation.
Stage 1: Your Sleep Entry Point
This is the drowsy transition zone where you're not quite awake but not fully asleep either. It typically lasts just 1-5 minutes and represents only about 5% of your night.
Your muscles start relaxing, your heartbeat slows, and those weird "falling" sensations might kick in. Totally normal - those are called hypnic jerks.
What's Happening In Your Brain
Your brain waves shift from alert alpha waves to slower theta waves. You're still aware enough that a door closing or someone calling your name will snap you back to full consciousness.
This stage is like the loading screen before the main game. Your body tests the waters, checking if it's safe to go deeper into sleep mode.
Why You Might Get Stuck Here
If you're tossing and turning for hours in this light sleep zone, anxiety or stress could be the culprit. Your nervous system stays too activated to progress deeper.
Creating a calming pre-bed routine helps. Consider incorporating meditation techniques to quiet your mind before sleep. Some people find meditation aids helpful for establishing this practice.
Stage 2: Where You Spend Most Time
Welcome to the main event. Stage 2 accounts for roughly 45-55% of your total sleep time, making it your body's favorite hangout spot.
Your body temperature drops, eye movements stop completely, and your heart rate becomes more regular. You're definitely asleep now, though not in the deepest phase yet.
The Memory Filing System
During stage 2, your brain generates something called "sleep spindles" - brief bursts of electrical activity that act like a mental filing cabinet. They help sort and store the day's information.
These spindles also block out external noise and sensations, creating a protective barrier so random sounds don't wake you. Pretty clever design, right?
Why This Stage Matters For Learning
People who consistently get quality stage 2 sleep show better memory recall and learning ability. Your brain is literally processing and organizing everything you experienced that day.
If you're a student or learning new skills, protecting this stage becomes crucial. Fragmented sleep here directly impacts your ability to retain information.
The connection between improving sleep quality and cognitive performance is well-documented in research.
Stage 3: Deep Sleep Recovery Mode
This is where the magic happens. Stage 3, also called slow-wave or delta sleep, is your body's primary repair and restoration phase.
Your brain produces slow, powerful delta waves. Waking someone from this stage is tough, and if you do, they'll be groggy and confused for several minutes.
Your Body's Maintenance Window
Blood pressure drops significantly, breathing becomes deep and rhythmic, and your muscles completely relax. This is when growth hormone gets released for tissue repair and muscle building.
If you've been hitting the gym or doing home workouts, this stage is where your muscles actually grow and recover. No deep sleep means no gains, simple as that.
The Brain Cleaning Crew
Scientists discovered that during deep sleep, your brain's waste removal system (glymphatic system) kicks into high gear. It flushes out toxins and harmful proteins that accumulated during waking hours.
This cleaning process may help prevent neurodegenerative diseases. Think of it as your brain's nightly maintenance routine that keeps it running smoothly for decades.
How Much Deep Sleep Do You Need?
Young adults typically spend 15-20% of the night here, though this decreases with age. In your first sleep cycles, you might get 20-40 minutes of deep sleep.
Quality matters more than quantity. Even small amounts of uninterrupted deep sleep can provide significant benefits compared to fragmented attempts.
Supporting your body's recovery with proper nutrition and quality supplements can enhance the benefits you get from deep sleep stages.
REM Sleep: The Dream Factory
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep is where things get weird and wonderful. Your brain becomes almost as active as when you're awake, yet your muscles are temporarily paralyzed.
This paralysis is a safety feature. Without it, you'd physically act out your dreams, which could be dangerous for you and anyone sleeping nearby.
Behind Your Closed Eyelids
Your eyes dart rapidly back and forth beneath your eyelids, scanning the dreamscape your brain creates. Brain waves look remarkably similar to waking patterns.
Most vivid, memorable dreams happen during REM sleep. The longer you sleep, the longer these REM periods become, especially in the second half of the night.
Why Your Brain Needs REM
This stage handles emotional processing and regulation. It's like overnight therapy where your brain works through feelings and experiences from the day.
REM sleep also strengthens complex memory connections and boosts creativity. Ever wake up with a solution to a problem that stumped you yesterday? Thank REM sleep.
The REM Pattern Throughout Night
You don't hit REM until about 90 minutes after falling asleep. Early cycles might give you just 10-15 minutes, but later ones can last up to an hour.
This is why cutting your sleep short by even an hour can disproportionately reduce your REM sleep, since you're missing those longer late-night cycles.
Understanding how sleep stages work together helps you appreciate why timing matters as much as duration.
How Sleep Cycles Progress Through Night
Here's where it all comes together. Sleep stages don't just happen randomly - they follow a predictable pattern that repeats throughout the night.
A typical cycle goes: Stage 1 → Stage 2 → Stage 3 → Stage 2 → REM. Then it loops back, usually skipping Stage 1 on subsequent cycles.
First Half Versus Second Half
Your early sleep cycles are deep sleep heavy. Your body prioritizes physical recovery first, spending more time in Stage 3 when you need it most.
As night progresses, deep sleep periods shrink while REM periods expand. By your last cycle before waking, you might be in REM for 45-60 minutes.
The 90-Minute Rule (Sort Of)
Each cycle averages 90 minutes, but it's not an exact science. Your cycles might run anywhere from 70 to 120 minutes depending on various factors.
Those apps claiming to calculate "perfect" wake times are making educated guesses at best. Individual variation is too significant for precise predictions.
Why 7-9 Hours Isn't Arbitrary
The recommendation for adults to get 7-9 hours exists because that's typically how long it takes to complete 4-6 full cycles, giving you adequate time in all stages.
Sleeping exactly 90-minute multiples won't magically optimize your sleep if you're only getting 4.5 hours total. You need enough cycles, period.
What Disrupts Your Sleep Stages
Plenty of factors can throw a wrench in your sleep cycle machinery. Understanding them helps you take control of your sleep quality.
Age Changes Everything
Babies enter REM directly and spend half their sleep there. As you age, deep sleep gradually decreases and sleep becomes more fragmented.
Older adults often need daytime naps to compensate for lighter, less efficient nighttime sleep. This isn't laziness - it's biology.
Alcohol's Deceptive Effects
Sure, that nightcap might help you fall asleep faster. But alcohol suppresses REM sleep in the first half of the night, then causes multiple awakenings as it metabolizes.
You might spend 8 hours in bed but wake feeling unrested because you missed crucial REM periods. The trade-off isn't worth it.
The Caffeine Time Bomb
Coffee has its benefits, but timing matters. Caffeine stays in your system for 6-8 hours, reducing deep sleep quality even if you fall asleep fine.
That 3 PM espresso could still be messing with your Stage 3 sleep at 11 PM. Consider cutting off caffeine after lunch for better results.
Stress And The Sleep Trap
Anxiety keeps you stuck in lighter sleep stages. Your nervous system stays too activated to transition into deeper, more restorative phases.
The irony is brutal: stress makes you need quality sleep more, but also makes it harder to get. Breaking this cycle often requires addressing daytime stress management.
Your Sleep Environment
Room temperature ideally sits between 65-72°F (18-22°C). Too hot or cold prevents smooth stage transitions, especially into deep sleep.
Light exposure, even small amounts, can suppress melatonin and disrupt your circadian rhythm. Invest in proper blackout solutions for your bedroom.
Optimize Your Sleep Architecture
Ready to actually improve your sleep stages? These strategies are backed by research and, more importantly, they work in real life.
Lock In Your Schedule
Your circadian rhythm thrives on consistency. Going to bed and waking at the same time daily - yes, even weekends - trains your body when to initiate sleep cycles.
A 30-60 minute wind-down routine signals your body that Stage 1 is approaching. This could include reading, light stretching, or relaxation techniques.
Master Light Exposure
Get bright light exposure within 30 minutes of waking. This anchors your circadian rhythm and promotes deeper sleep 14-16 hours later.
At night, dim the lights 2-3 hours before bed. Avoid screens or use blue light filters. Your brain interprets bright light as "daytime," delaying melatonin release.
Time Your Meals Right
Heavy meals within 3-4 hours of bedtime force your body to prioritize digestion over sleep stages. You might fall asleep but won't progress efficiently through cycles.
If you need a snack, choose something light with protein or complex carbs. Some people find specific foods help promote better sleep.
Exercise Smart, Not Hard
Regular cardiovascular exercise significantly improves deep sleep quality. But timing matters - intense workouts within 3-4 hours of bed can be too stimulating.
Morning or afternoon sessions work best. They build natural sleep pressure without interfering with your body's wind-down process.
For home exercise options, consider investing in quality gym equipment or a treadmill that makes consistent workouts convenient.
Consider Strategic Supplementation
Certain supplements can support sleep quality when used correctly. Melatonin helps regulate circadian rhythm, especially useful for shift workers or jet lag.
Magnesium promotes muscle relaxation and may ease the transition to deeper sleep stages. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Quality matters when choosing supplements - look for third-party tested products from reputable manufacturers.
For those wanting to deepen their understanding of sleep optimization, evidence-based health books can provide additional strategies and insights.
Sleep Disorders That Break Cycles
Sometimes lifestyle changes aren't enough because an underlying disorder is sabotaging your sleep stages. Recognizing these issues is the first step toward fixing them.
Sleep Apnea's Hidden Damage
Obstructive sleep apnea causes repeated breathing interruptions throughout the night. Each pause triggers a micro-awakening that prevents you from reaching or staying in deep sleep.
People with untreated apnea can spend 8+ hours in bed but get almost no Stage 3 sleep. The result? Crushing daytime fatigue regardless of time spent sleeping.
Warning signs include loud snoring, observed breathing pauses, morning headaches, and excessive daytime sleepiness. If this sounds familiar, get evaluated.
Restless Leg Syndrome
This condition creates an irresistible urge to move your legs, especially when lying down. The constant movement fragments your sleep cycles before they can deepen.
RLS may be linked to iron deficiency or neurological factors. Treatment can dramatically improve sleep quality once the underlying cause is addressed.
When Insomnia Goes Chronic
Chronic insomnia isn't just trouble falling asleep. Many insomniacs can initiate sleep but wake frequently, preventing proper cycle completion.
If anxiety keeps your nervous system in alert mode, you might never transition past light sleep stages. This creates a vicious cycle of poor sleep causing more anxiety.
Getting Professional Help
If you consistently wake exhausted despite adequate time in bed, snore heavily, experience breathing pauses, or feel extreme daytime sleepiness, see a sleep specialist.
A sleep study (polysomnography) can identify exactly which stages are being disrupted and why. This data allows for targeted treatment instead of guessing.
Don't normalize bad sleep. Your body needs proper rest to function, and effective treatments exist for most sleep disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many sleep stages are there?
There are 4 main sleep stages: 3 non-REM stages (light, intermediate, and deep sleep) plus REM sleep where dreaming occurs. Each stage serves unique functions for your body and brain.
How long is one complete sleep cycle?
A typical sleep cycle lasts about 90 minutes, though it can range from 70 to 120 minutes. Most people complete 4-6 cycles during a full night's sleep.
Which sleep stage is most important?
All stages matter, but stage 3 (deep sleep) handles physical recovery and immune function, while REM sleep processes emotions and memories. You need both for optimal health.
Why do I wake up tired even after 8 hours?
You might be experiencing interrupted sleep cycles due to sleep disorders like apnea, poor sleep environment, stress, or lifestyle factors that prevent you from reaching deeper sleep stages.
Can I improve my sleep stages naturally?
Yes! Consistent sleep schedules, proper light exposure, avoiding caffeine late in the day, and creating a cool, dark bedroom can significantly improve your progression through sleep stages.
Conclusion
Understanding your sleep stages transforms how you think about rest. It's not just about clocking hours - it's about giving your body the opportunity to progress smoothly through each critical phase.
Every stage serves a purpose. Stage 3 rebuilds your body physically while REM sleep processes emotions and consolidates memories. Skip or fragment these stages, and you'll feel the effects no matter how long you stayed in bed.
Your body knows what it needs to do each night. Your job is simply to create the conditions that let it happen. Sweet dreams and deep cycles ahead!









