What Is Omega-3 And Its Importance For Health
Discover everything about omega-3: what it is, benefits for heart and brain health, best food sources, when to supplement, and how to include it in your daily diet for a healthier life.
If you've ever wondered why so many health experts rave about omega-3, get ready to discover why this "good fat" is considered one of the most crucial nutrients for our health. From protecting our hearts to boosting our focus and concentration, omega-3 plays fundamental roles you might never have imagined.
Here's the catch: our bodies can't produce this essential substance on their own. That means we need to get it through food or supplementation. And here's the million-dollar question: are you getting enough omega-3? Most Americans aren't, and this could be directly impacting your quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, you'll understand exactly what omega-3 is, discover its main scientifically-proven benefits, learn about the best food sources, and find out when supplementation is really worth it. Let's turn this knowledge into practical actions for your health.
Table of Contents
- What Is Omega-3 and Why It's Essential
- The 3 Main Types of Omega-3
- Key Health Benefits
- Omega-3 and Heart Health
- Brain and Memory Benefits
- Best Food Sources
- When Supplementation Is Necessary
- Recommended Dosage by Age
- Potential Side Effects
What Is Omega-3 and Why It's Essential
Omega-3 is a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid - a "good fat" that our bodies need to function properly. The most important characteristic of omega-3 is that it's considered essential, meaning our bodies can't naturally produce it in sufficient quantities.
These substances play crucial roles in cell membrane structure and metabolic processes. They're fundamental for maintaining proper brain function, nerve impulse transmission, and various anti-inflammatory processes throughout the body.
What's interesting is that omega-3 fatty acids get their name from their specific chemical structure: they have a double bond between the third and fourth carbon atoms counted from the methyl end of the molecule. This unique configuration is what gives them their special beneficial properties.
Epidemiological studies show that populations consuming more omega-3 - like the Japanese and Mediterranean peoples - have lower rates of cardiovascular and inflammatory diseases. This isn't a coincidence: it's proven science.
When you're looking to optimize your health through nutrition, quality supplements can make a significant difference. You can find excellent omega-3 supplements that provide the concentrated nutrition your body needs.
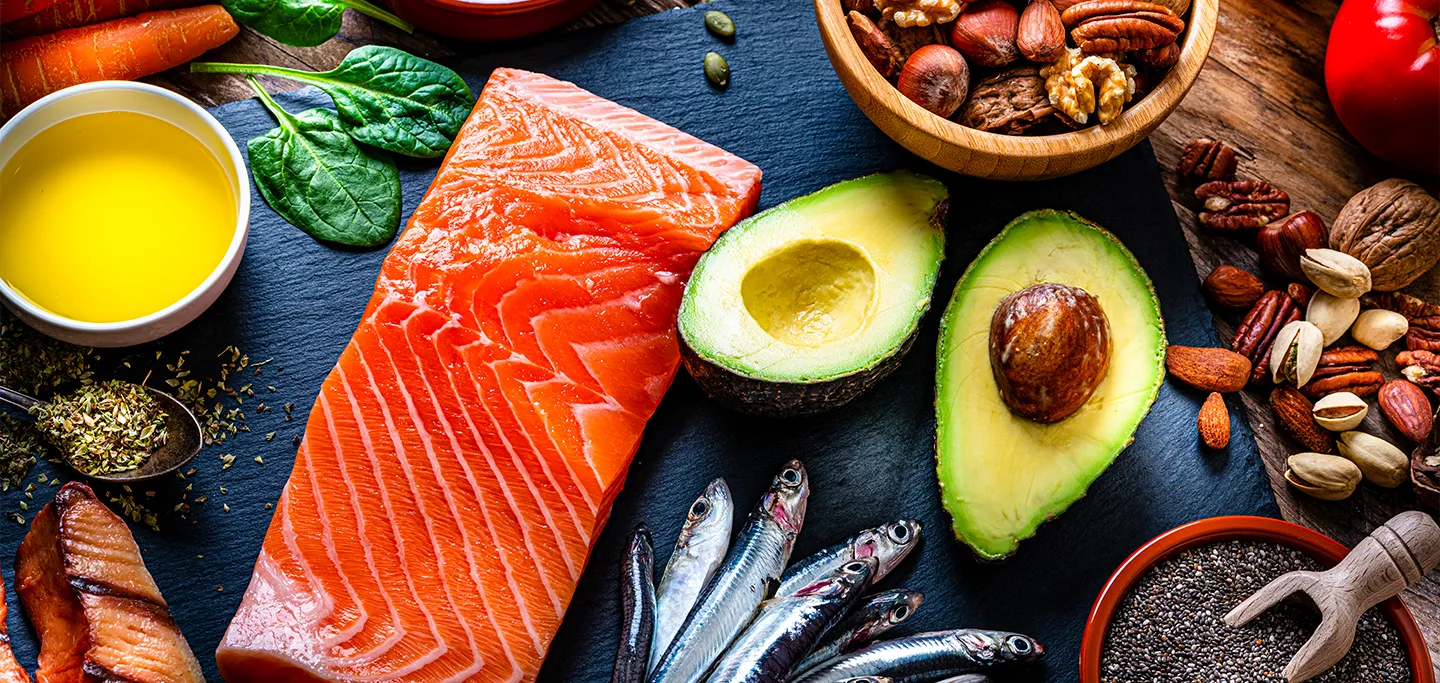

The 3 Main Types of Omega-3
Not all omega-3 is created equal. There are three main types, each with specific functions in our bodies:
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)
EPA is known primarily for its anti-inflammatory effects and cardiovascular benefits. It's found mainly in cold-water fish and works directly to reduce inflammatory processes throughout the body, helping prevent chronic diseases.
DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)
DHA is the "brain fuel." About 60% of our brain is composed of fat, and DHA represents a significant portion of that composition. It's fundamental for neurological development, memory, and cognitive functions.
ALA (Alpha-linolenic Acid)
ALA is found primarily in plant sources like flaxseeds and chia seeds. While important, our bodies need to convert ALA into EPA and DHA to get maximum benefits - and this conversion is quite limited, usually less than 10%.
That's why experts recommend prioritizing direct sources of EPA and DHA, which are cold-water fish. For vegetarians and vegans, supplementation with marine algae can be an interesting alternative.
For those following specific dietary approaches, understanding how omega-3 fits into different eating plans is crucial. Learn more about ketogenic diets and how healthy fats play a vital role.
Key Health Benefits
The benefits of omega-3 are extensive and well-documented by science. Here are the main positive effects you can expect:
Powerful Anti-inflammatory Action
Omega-3 reduces the production of inflammatory substances like eicosanoids and cytokines. This is especially useful for people with rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other chronic inflammatory conditions.
Complete Cardiovascular Protection
Studies show that omega-3 can reduce triglycerides by up to 30%, improve arterial function, and decrease the risk of cardiac arrhythmias. It's like "life insurance" for your heart.
Immune System Strengthening
Omega-3 helps regulate important immune system cells, such as T and B cells, while improving the phagocytic capacity of macrophages - cells specialized in destroying harmful invaders.
Mental Health Improvement
Research indicates that omega-3 can help prevent and treat depression by increasing the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
If you're into fitness, you'll be glad to know that the best home workouts for weight loss become even more effective when combined with proper nutrition, including omega-3.
When it comes to overall wellness, incorporating omega-3 is just one piece of the puzzle. For comprehensive health optimization, explore wellness products that can support your journey to better health.

Omega-3 and Heart Health
The relationship between omega-3 and heart health is one of the most studied and proven areas in medical science. The cardiovascular benefits are impressive and multiple.
Triglyceride Reduction
Omega-3 can reduce blood triglyceride levels by 25-30%. Elevated triglycerides are an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease, especially when combined with other factors like high cholesterol.
Improved Arterial Function
Omega-3 fatty acids improve arterial elasticity and reduce atherosclerotic plaque formation. This means better blood flow and lower risk of heart attack and stroke.
Blood Pressure Control
Studies show that regular omega-3 supplementation can result in modest but significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Arrhythmia Prevention
Perhaps one of the most impressive benefits is omega-3's ability to stabilize heart rhythm, reducing the risk of dangerous arrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac death.
The Mediterranean diet, rich in fatty fish and other omega-3 sources, is associated with up to a 30% reduction in major cardiovascular events. This demonstrates the preventive power of this nutrient when consistently incorporated into your diet.
Understanding how different nutrients work together is key. Learn about proteins and their importance for health to create a well-rounded nutritional approach.
Brain and Memory Benefits
The brain is the organ that benefits most from omega-3, especially DHA. The relationship between this nutrient and brain function is fascinating and crucial for people of all ages.
Neurological Development
During pregnancy and the first years of life, DHA is fundamental for nervous system development. Mothers who consume adequate omega-3 during pregnancy have children with better cognitive development and lower risk of disorders like ADHD.
Protection Against Cognitive Decline
Omega-3 can help slow age-related cognitive decline. Studies suggest that people with higher blood DHA levels have a lower risk of developing Alzheimer's and other forms of dementia.
Memory and Concentration Improvement
Omega-3 supplementation, especially DHA, can improve working memory, concentration ability, and information processing. This is especially relevant for students and professionals who depend on high mental performance.
Mood Regulation
Omega-3 influences the production of neurotransmitters responsible for mood and well-being. People deficient in this nutrient may be more prone to depression and anxiety.
For those looking to further improve mental performance, combining omega-3 with practices like meditation can enhance brain benefits.
Mental wellness also benefits from quality sleep. Discover more about sleep importance and how to improve sleep quality naturally.
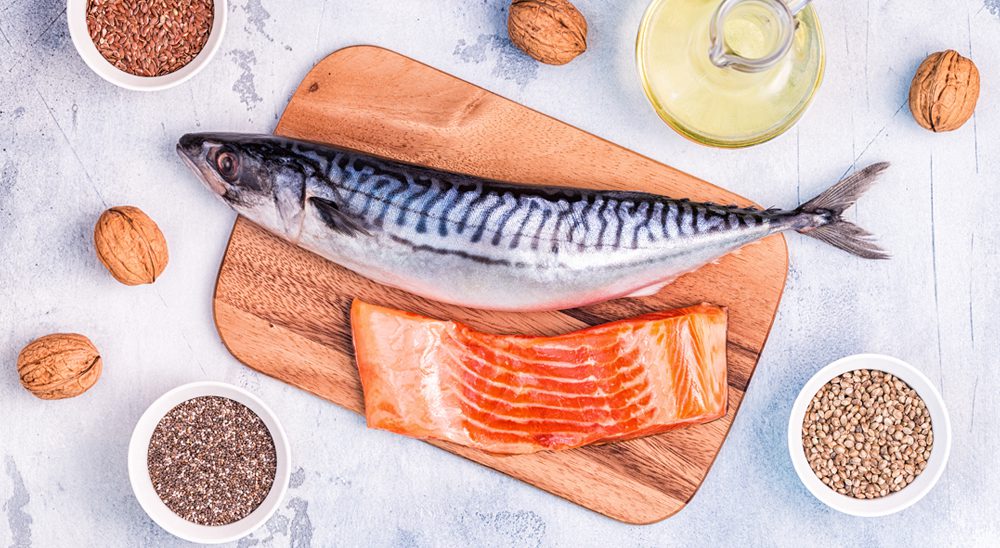

Best Food Sources
Nature provides us with excellent sources of omega-3, and knowing them is fundamental for making smart food choices. Let's organize by category and concentration:
Animal Sources (EPA and DHA)
| Fish | Omega-3 per 100g | Availability | Average Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon | 2,260mg | Easy | High |
| Sardines | 1,480mg | Very Easy | Low |
| Tuna | 1,280mg | Easy | Medium |
| Mackerel | 1,840mg | Moderate | Medium |
Plant Sources (ALA)
- Flaxseed oil: 53,300mg per 100g
- Flaxseeds: 22,800mg per 100g
- Chia seeds: 17,800mg per 100g
- Walnuts: 9,080mg per 100g
- Canola oil: 9,140mg per 100g
Practical Tips for Including in Your Diet
For fish: Consume at least 2 servings per week, prioritizing smaller fish like sardines (lower mercury concentration). Prepare grilled, baked, or steamed - avoid frying which can degrade omega-3.
For seeds: Grind flaxseeds before consumption for better absorption. Chia seeds can be consumed whole, added to yogurt, smoothies, or salads.
If you're seeking more complete nutrition, check out the top 10 best natural foods to further diversify your diet.
For those following specific dietary approaches, understanding low-carb diets can help you incorporate omega-3 rich foods effectively.
When Supplementation Is Necessary
While food should always be the first choice, there are specific situations where omega-3 supplementation can be beneficial or even necessary.
Signs of Deficiency
Some symptoms may indicate low omega-3 levels in the body:
- Dry, flaky skin
- Frequent dry eyes
- Joint stiffness
- Memory and concentration problems
- Frequent mood swings
- Excessive fatigue
Groups That Benefit Most
Pregnant and nursing women: Increased needs for baby's neurological development. Seniors: Higher risk of cognitive decline and cardiovascular problems. Vegetarians/vegans: Difficulty obtaining sufficient EPA and DHA. People with inflammatory diseases: Arthritis, Crohn's disease, etc.
How to Choose a Good Supplement
Look for supplements that contain:
- High concentration of EPA and DHA (not just "fish oil")
- Purity certification (mercury and contaminant-free)
- Sustainable source (responsible fishing)
- Natural triglyceride form (better absorption than ethyl esters)
When choosing supplements, quality matters tremendously. High-quality omega-3 supplements can provide the concentrated nutrition your body needs without the concerns about mercury or other contaminants.
For a comprehensive approach to supplementation, learn about the best supplement brands in 2025 to make informed choices.
Recommended Dosage by Age
Omega-3 needs vary significantly according to age, health conditions, and specific goals. Here are evidence-based recommendations:
Infants and Children
- 0-12 months: 500mg/day (mainly through breast milk)
- 1-3 years: 700mg/day
- 4-8 years: 900mg/day
- 9-13 years: 1,000-1,200mg/day
Teens and Adults
- Girls 14-18 years: 1,100mg/day
- Boys 14-18 years: 1,600mg/day
- Adult women: 1,100mg/day
- Adult men: 1,600mg/day
Special Situations
- Pregnant women: 1,400mg/day (focusing on DHA)
- Nursing mothers: 1,300mg/day
- Seniors: 1,000-2,000mg/day (for cognitive protection)
- Athletes: 2,000-3,000mg/day (for muscle recovery)
Practical Equivalents
To reach these amounts through food:
- 1 serving of salmon (150g) = approximately 3,400mg
- 1 can of sardines (120g) = approximately 1,780mg
- 2 tablespoons of chia seeds = approximately 3,560mg of ALA
It's important to remember that our bodies convert only 5-10% of ALA to EPA/DHA, so plant sources need to be consumed in larger quantities.
For athletes looking to optimize recovery, combining omega-3 with proper pre and post-workout nutrition can enhance performance and recovery.

Potential Side Effects
Like any nutrient, omega-3 can cause adverse effects when consumed in excess or by people with specific conditions. It's essential to know these risks to use safely.
Common Side Effects (doses > 3,000mg/day)
- Digestive problems: nausea, diarrhea, abdominal cramps
- Fishy breath: especially common with low-quality supplements
- Excessive gas: can cause abdominal discomfort
- Reflux: some people may experience heartburn
More Serious Risks
Increased bleeding risk: Omega-3 has natural anticoagulant properties. People taking medications like warfarin, aspirin, or clopidogrel should exercise special caution and always consult a doctor.
Drug interactions: May potentiate the effect of blood pressure medications, requiring dosage adjustments.
LDL increase: At very high doses (above 4,000mg/day), some people may experience elevated LDL cholesterol.
Contraindications
- People with bleeding disorders
- Those undergoing surgery (discontinue 2 weeks prior)
- Those allergic to fish or seafood (for fish oil supplements)
- People with uncontrolled diabetes (may affect glycemic control)
How to Minimize Side Effects
- Start with low doses and increase gradually
- Take with food to reduce digestive problems
- Choose quality supplements to avoid fishy odor
- Keep refrigerated to preserve quality
- Consult a professional before starting, especially if taking medications
The golden rule is: moderation and professional guidance. Quality supplements from reputable sources help ensure you get the benefits while minimizing risks.
Integrating Omega-3 Into Your Routine
Now that you know all the benefits and precautions, it's time to put this knowledge into practice. The key is making sustainable changes that become a natural part of your lifestyle.
Practical Strategies for Daily Life
Plan your meals: Reserve at least two meals per week to include omega-3 rich fish. Canned sardines are practical, economical, and nutritious - perfect for quick snacks or salads.
Diversify sources: Alternate between animal and plant sources. At breakfast, add chia seeds to yogurt. At lunch, include a salmon fillet. For snacks, a handful of walnuts.
Combine with other healthy habits: Omega-3 works even better when combined with an active lifestyle. If you're thinking about gaining muscle mass, this nutrient can accelerate post-workout recovery.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Observe how your body responds. Improvements in sleep quality, energy, and concentration usually appear within the first 4-6 weeks. If you have specific conditions like cardiovascular problems, consider getting blood tests to monitor levels.
For those seeking a comprehensive health approach, exploring specialized resources can be valuable. Quality diet and nutrition books can provide deeper insights into how nutrients like omega-3 fit into overall wellness strategies.
The Next Step
Omega-3 isn't just another "trendy supplement" - it's an essential nutrient backed by decades of scientific research. From protecting your heart to keeping your brain sharp, the benefits are real and measurable.
The good news is that incorporating omega-3 into your life doesn't have to be complicated or expensive. Start with small changes: replace a processed snack with a handful of walnuts, add sardines to your shopping list, or try adding chia seeds to your breakfast.
Remember: consistency is more important than perfection. It's better to consume a moderate amount of omega-3 regularly than large amounts sporadically.
Your future health will thank you for the choices you make today. And who knows? In a few months, you might realize that those small changes resulted in significant improvements in your quality of life, energy, and overall well-being.
For a holistic approach to health, consider how omega-3 fits with other important factors like understanding coffee's effects on health and maintaining healthy sleep patterns.
The journey to optimal health is ongoing, and omega-3 is a powerful ally in that journey. Whether through food sources or quality supplementation, making this essential nutrient a regular part of your routine is an investment in your long-term health and vitality.